Nodejs Complete Guide
Example :
const http = require('http')
const hostname = '127.0.0.1'
const port = 3000
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.statusCode = 200
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain')
res.end('Hello World\n')
})
server.listen(port, hostname, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`)
})Install :
npm iInstalling package :
npm install <package-name>Installing Specific version :
npm install <package-name>@<version>Update :
npm updateUpdating package :
npm update <package-name>Running :
npm run watch
npm run dev
npm run prodRestart the application automatically
npm i -g nodemonnpm i --save-dev nodemonRun the application using the nodemoncommand followed by the application's file name:
nodemon app.jsUsing REPL
nodeNode.js with Express.js
Installation
npm init
or
npm init -y
npm init --yesInstall express
npm install expressExample :
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!')
})
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`)
})Save as index.js (filename.js)
Run the application using the nodecommand followed by the application's file name:
node index.jsStackblitz Link :
https://stackblitz.com/edit/node-nzw4cm?file=index.js
Node.js with dotenv
Install :
npm i dotenvUsage :
Create .env file
PORT = 3000
KEY = "values"Import and configure dotenv:
require('dotenv').config()
// console.log(process.env.PORT)Examples :
https://github.com/dotenv-org/examples
Node.js with Typescript
Initialize and Install Typescript
npm init -y
npm install -D typescript @types/nodeUpdate the package.json with a build script and change the type to module.
{
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc"
},
}Create a tsconfig.json file and use the NodeNext option to handle ES Modules with interop between CommonJS modules.
{
"compilerOptions": {
"module": "NodeNext",
"moduleResolution": "NodeNext",
"target": "ES2020",
"sourceMap": true,
"outDir": "dist",
},
"include": ["src/**/*"],
}Use ES Modules
//hello.ts
export const hello = 'Hello World!';
//index.ts
import { hello } from './hello.js';Use CommonJS Modules
//hello.cts
module.exports = 'Hey!';
//index.ts
import hola from './hello.cjs';Next run
npm run build
node dist/index.jsGraphQL with Node.js and Express.js
Create a directory and make that your working directory.
mkdir example-app
cd example-appUse npm init to create packge.json in your application
npm init
or
npm init -yFist install expressusing npm install
npm i expressNext create index.js file
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!')
})
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`);
})Now run the project
node index.jsOutput will get : Example app listening on port 3000
Then, load http://localhost:3000/in a browser to see the output.
Now will serve static files in project by creating public folder and adding index.html in it.
Next updating index file with below code.
...
const path = require('path')
app.use('/', express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')))
...Next add express-graphpql, and graphqlusing npm install in the project
npm i express-graphpql graphqlNow update index.js with following
...
const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`);
// The root provides a resolver function for each API endpoint
const root = {
hello: () => {
return 'Hello world!';
},
};
...
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
}));
....Here is the final index.js file with complete code
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = 3000
const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`);
// The root provides a resolver function for each API endpoint
const root = {
hello: () => {
return 'Hello world!';
},
};
const path = require('path')
app.use('/', express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')))
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!')
})
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port} and GraphQL server listening on port ${port}/graphql`);
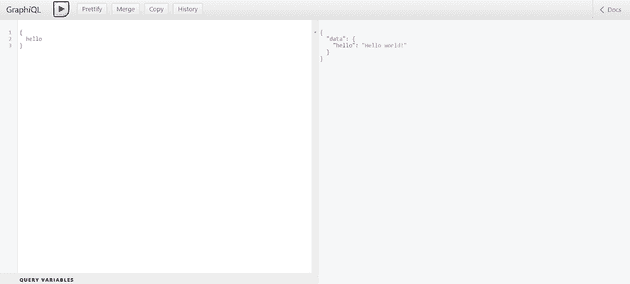
})Now run the project and you will see output : Example app listening on port 3000 and GraphQL server listening on port 3000/graphql
Then load http://localhost:3000/graphql in a browser to see the output.
Complete code available here - https://github.com/manthanank/graphql-nodejs-expressjs